User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Agilent Technologies 16750A/B Logic Analyzer
- Agilent Technologies 16750A/B Logic Analyzer
- Contents
- Getting Started
- Step 1. Connect the logic analyzer to the device under test
- Step 2. Choose the sampling mode
- Step 3. Format labels for the probed signals
- Step 4. Define the trigger condition
- Step 5. Run the measurement
- Step 6. Display the captured data
- For More Information...
- Example: Timing measurement on counter board
- Example: State measurement on counter board
- Task Guide
- Probing the Device Under Test
- Choosing the Sampling Mode
- To select transitional timing or store qualified
- Formatting Labels for Logic Analyzer Probes
- Setting Up Triggers and Running Measurements
- Displaying Captured Data
- Using Symbols
- Printing/Exporting Captured Data
- Cross-Triggering
- Solving Logic Analysis Problems
- Saving and Loading Logic Analyzer Configurations
- Reference
- The Sampling Tab
- The Format Tab
- Importing Netlist and ASCII Files
- The Trigger Tab
- The Symbols Tab
- Error Messages
- Must assign Pod 1 on the master card to specify actions for flags
- Branch expression is too complex
- Cannot specify range on label with clock bits that span pod pairs
- Counter value checked as an event, but no increment action specified
- Goto action specifies an undefined level
- Maximum of 32 Channels Per Label
- Hardware Initialization Failed
- Must assign another pod pair to specify actions for flags
- No more Edge/Glitch resources available for this pod pair
- No more Pattern resources available for this pod pair
- No Trigger action found in the trace specification
- Slow or Missing Clock
- Timer value checked as an event, but no start action specified
- Trigger function initialization failure
- Trigger inhibited during timing prestore
- Trigger Specification is too complex
- Waiting for Trigger
- Analyzer armed from another module contains no "Arm in from IMB" event
- Specifications and Characteristics
- Concepts
- Understanding Logic Analyzer Triggering
- Understanding State Mode Sampling Positions
- Getting Started
- Glossary
- Index
147
Chapter 3: Reference
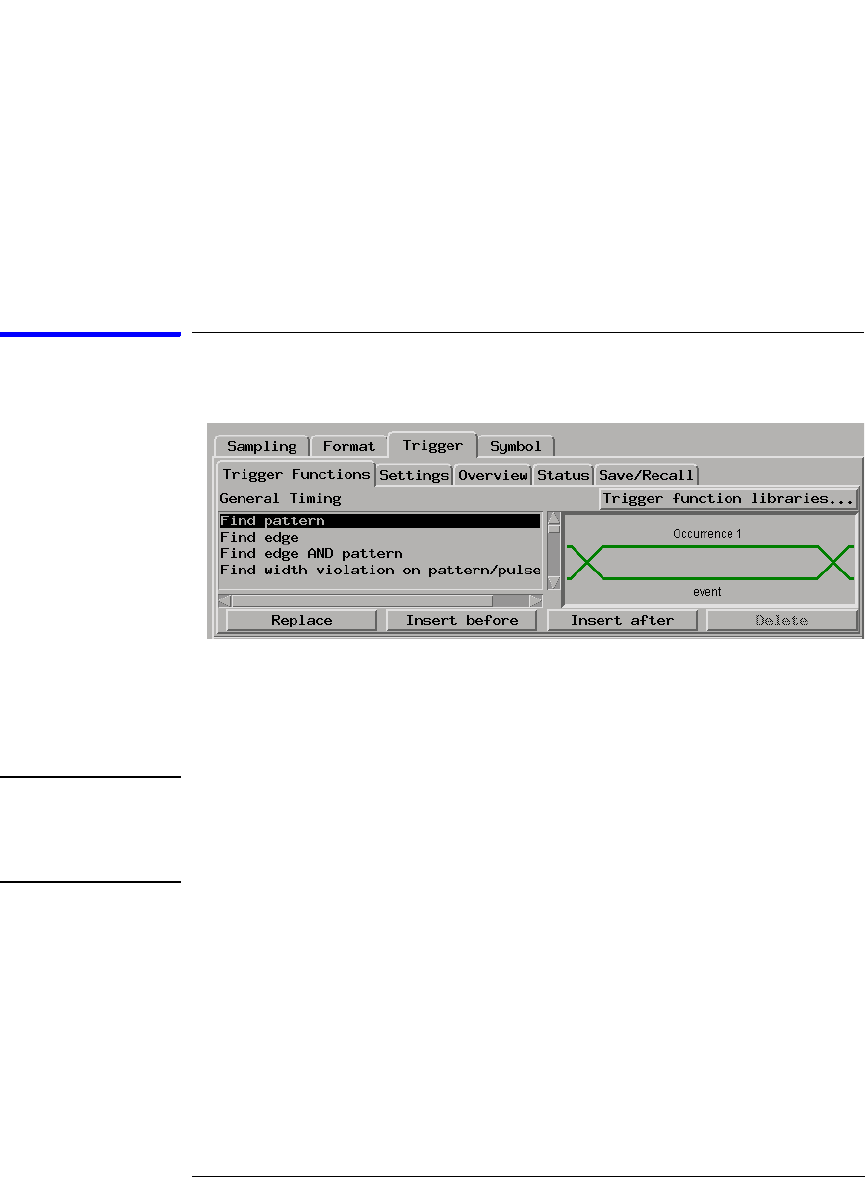
The Trigger Tab
• “Save/Recall Subtab” on page 157
See Also “Understanding Logic Analyzer Triggering” on page 192
“Setting Up Triggers and Running Measurements” on page 64
“Editing the Trigger Sequence” on page 72
Trigger Functions Subtab
Trigger functions provide a simple way to set up the analyzer to trigger
on common events and conditions. A library of functions is available for
both state and timing measurements.
NOTE: Each trigger function requires at least one internal sequence level (see
page 72), and in some cases, multiple levels. The number of levels used by
each function can be seen by breaking down or expanding the trigger
function.
• “General Timing Trigger Functions” on page 148
• “General State Trigger Functions” on page 150
• “Advanced Trigger Functions” on page 153
See Also • “Using Trigger Functions” on page 65
• “Editing Advanced Trigger Functions” on page 78










