Technical data
22 Agilent 6200 Series TOF and 6500 Series Q-TOF LC/MS System Concepts Guide
1Overview
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI)
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI)
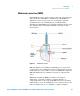
APCI is a gas-phase chemical ionization process. The APCI
technique passes LC eluent through a nebulizing needle, which
creates a fine spray. The spray is passed through a heated
ceramic tube, where the droplets are fully vaporized (Figure 4).
The resulting gas/vapor mixture is then passed over a corona
discharge needle, where the solvent vapor is ionized to create
reagent gas ions. These ions in turn ionize the sample molecules
via a chemical ionization process. The sample ions are then
introduced into the capillary.
APCI requires that the analyte be in the gas phase for ionization
to occur. To vaporize the solvent and analyte, the APCI source is
typically operated at vaporizer temperatures of 400 to 500°C.
Figure 4 Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) source
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
++
++
++
++
++
++
++
nebulizer (sprayer)
HPLC inlet
vaporizer
(heater)
drying gas
capillary
corona
discharge
needle