User`s guide
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Getting Started
- Introduction and Measurement
- Phase Noise Basics
- Expanding Your Measurement Experience
- Starting the Measurement Software
- Using the Asset Manager
- Using the Server Hardware Connections to Specify the Source
- Setting GPIB Addresses
- Testing the 8663A Internal/External 10 MHz
- Testing the 8644B Internal/External 10 MHz
- Viewing Markers
- Omitting Spurs
- Displaying the Parameter Summary
- Exporting Measurement Results
- Absolute Measurement Fundamentals
- Absolute Measurement Examples
- Residual Measurement Fundamentals
- What is Residual Noise?
- Assumptions about Residual Phase Noise Measurements
- Calibrating the Measurement
- Measurement Difficulties
- Residual Measurement Examples
- FM Discriminator Fundamentals
- FM Discriminator Measurement Examples
- AM Noise Measurement Fundamentals
- AM Noise Measurement Examples
- Baseband Noise Measurement Examples
- Evaluating Your Measurement Results
- Advanced Software Features
- Reference Graphs and Tables
- Approximate System Noise Floor vs. R Port Signal Level
- Phase Noise Floor and Region of Validity
- Phase Noise Level of Various Agilent Sources
- Increase in Measured Noise as Ref Source Approaches DUT Noise
- Approximate Sensitivity of Delay Line Discriminator
- AM Calibration
- Voltage Controlled Source Tuning Requirements
- Tune Range of VCO for Center Voltage
- Peak Tuning Range Required by Noise Level
- Phase Lock Loop Bandwidth vs. Peak Tuning Range
- Noise Floor Limits Due to Peak Tuning Range
- Tuning Characteristics of Various VCO Source Options
- 8643A Frequency Limits
- 8644B Frequency Limits
- 8664A Frequency Limits
- 8665A Frequency Limits
- 8665B Frequency Limits
- System Specifications
- System Interconnections
- PC Components Installation
- Overview
- Step 1: Uninstall the current version of Agilent Technologies IO libraries
- Step 2: Uninstall all National Instruments products.
- Step 3: Install the National Instruments VXI software.
- Step 4: Install the National Instruments VISA runtime.
- Step 5: Install software for the NI Data Acquisition Software.
- Step 6: Hardware Installation
- Step 7. Finalize National Instruments Software Installation.
- Step 8: System Interconnections
- Step 9: Install Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributable Package use default settings
- Step 10: Install the Agilent I/O Libraries
- Step 11: Install the E5500 Phase Noise Measurement software.
- Step 12: Asset Configuration
- Step 13: License Key for the Phase Noise Test Set
- Overview
- PC Digitizer Performance Verification
- Preventive Maintenance
- Service, Support, and Safety Information
- Safety and Regulatory Information
- Safety summary
- Equipment Installation
- Environmental conditions
- Before applying power
- Ground the instrument or system
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers
- Maintenance
- Safety symbols and instrument markings
- Regulatory Compliance
- Declaration of Conformity
- Compliance with German noise requirements
- Compliance with Canadian EMC requirements
- Service and Support
- Return Procedure
- Safety and Regulatory Information
296 Agilent E5505A User’s Guide
11
AM Noise Measurement Fundamentals
Method 2: Double-Sided Spur
Method 2, example 1
Advantages
• Requires only one RF source (DUT)
• Calibration is done under actual measurement conditions so all
non-linearities and harmonics of the AM detector are calibrated out. The
double-sided spur method and the single-sided-spur method are the two
most accurate methods for this reason.
Disadvantages
• Required that the DUT have adjustable AM which may also be turned off.
• Requires the AM of the DUT to be extremely accurate; otherwise a
modulation analyzer, for manual measurement of AM sidebands is required.
Procedure
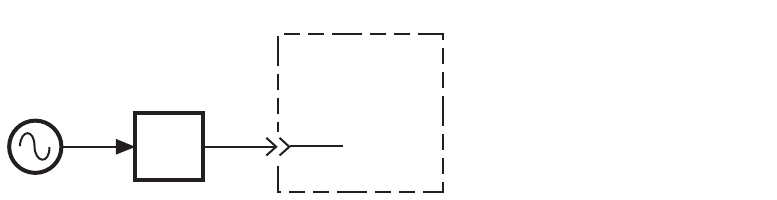
1
Connect circuit as shown in Figure 227, and tighten all connections. If the
N5500A Option 001 or N5507A is available, use one of the connection
diagrams described in “AM noise measurement block diagrams" on
page 287.
2
Measure the power which will be applied to the AM detector. It must be
between 0 and +23 dBm.
3
Measure the carrier-to-sideband ratio of the AM at the AM detector’s input
with an RF spectrum analyzer or modulation analyzer (Figure 228 on
page 297). The source should be adjusted such that the sidebands are
between –30 and –60 dB below the carrier with a modulation rate between
10 Hz and 20 MHz.
Figure 227 Double-Sided spur AM noise setup (method 2, example 1)
DUT
AM detector
Noise
input
Test set










