Programming instructions
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Title Page
- Chapter 1 Introduction to Programming
- Chapter 2 Programming Getting Started
- Chapter 3 Programming over HP-IB
- Chapter 4 Programming over RS-232-C
- Chapter 5 Programming and Documentation Conventions
- Chapter 6 Status Reporting
- Figure 6-1. Status Reporting Overview Block Diagram
- Table 6-1. Status Reporting Bit Definition
- Status Reporting Data Structures
- Status Byte Register (SBR)
- Service Request Enable Register (SRER)
- Trigger Event Register (TRG)
- Standard Event Status Register (SESR)
- Standard Event Status Enable Register (SESER)
- User Event Register (UER)
- Local Event Register (LCL)
- Operation Status Register (OPR)
- Limit Test Event Register (LTER)
- Mask Test Event Register (MTER)
- Histogram Event Register (HER)
- Arm Event Register (ARM)
- Error Queue
- Output Queue
- Message Queue
- Key Queue
- Clearing Registers and Queues
- Figure 6-3. Status Reporting Decision Chart
- Chapter 7 Installing and Using the Programmer's Reference
- Chapter 8 Programmer’s Quick Reference
- Warranty
- Index
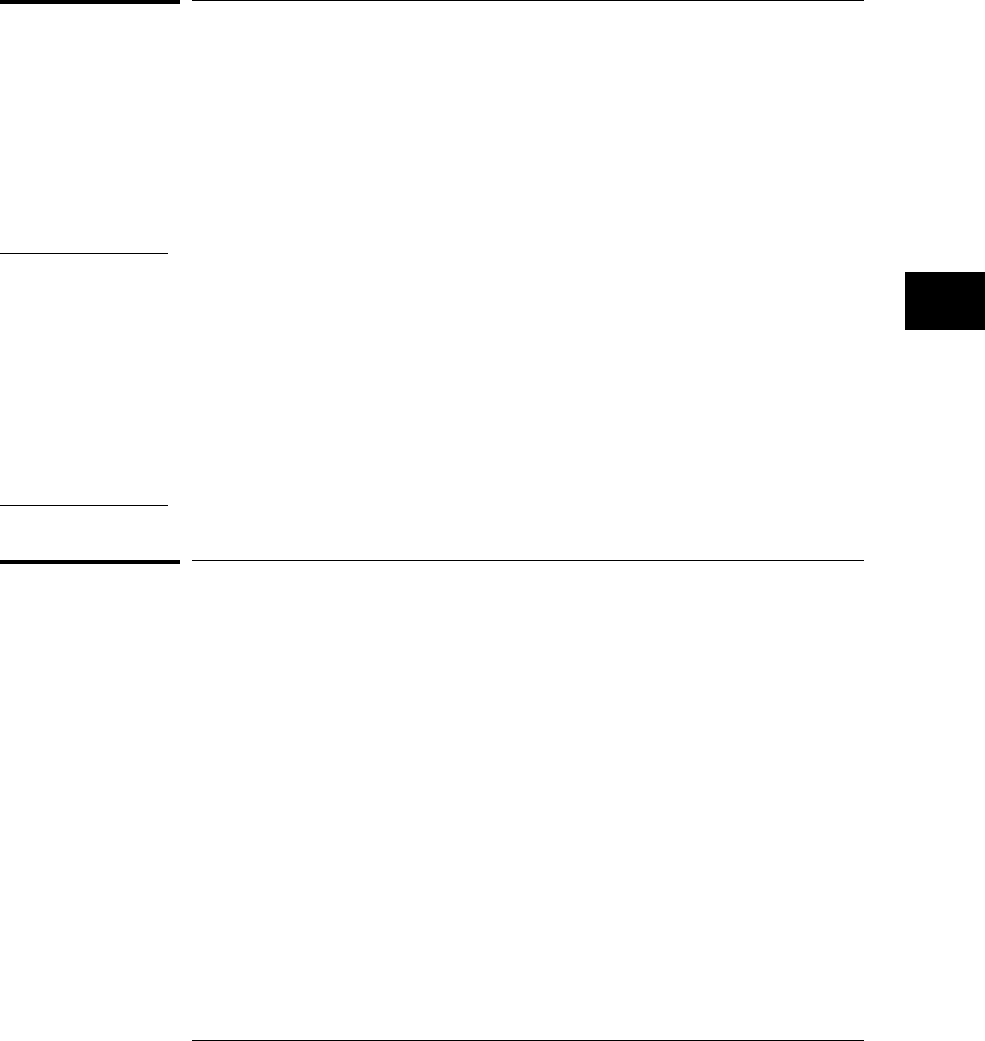
Service Request Enable Register (SRER)
Setting the Service Request Enable Register bits enable corresponding bits in
the Status Byte Register. These enabled bits can then set RQS and MSS (bit
6) in the Status Byte Register.
Bits are set in the Service Request Enable Register using the *SRE command
and the bits that are set are read with the *SRE? query.
Refer to figure 6-2.
Example The following example sets bit 4 (MAV) and bit 5 (ESB) in the Service
Request Enable Register.
OUTPUT 707;"*SRE 48"
This example uses the parameter “48” to enable the oscilloscope to generate
an SRQ interrupt under the following conditions:
•
When one or more bytes in the Output Queue set bit 4 (MAV).
•
When an enabled event in the Standard Event Status Register generates a
summary bit that sets bit 5 (ESB).
Trigger Event Register (TRG)
This register sets the TRG bit in the status byte when a trigger event occurs.
The TRG event register stays set until it is cleared by reading the register or
using the *CLS command. If your application needs to detect multiple
triggers, the TRG event register must be cleared after each one.
If you are using the Service Request to interrupt a program or controller
operation, each time the trigger bit is set you must then clear the event
register.
Status Reporting
Service Request Enable Register (SRER)
6-11