User's Manual
Deployment Guide 153
Chapter 10 HiveOS
You can deploy a single HiveAP and it will provide wireless access as an autonomous AP (access point). However, if
you deploy two or more HiveAPs in a hive, you can provide superior wireless access with many benefits. A hive is a
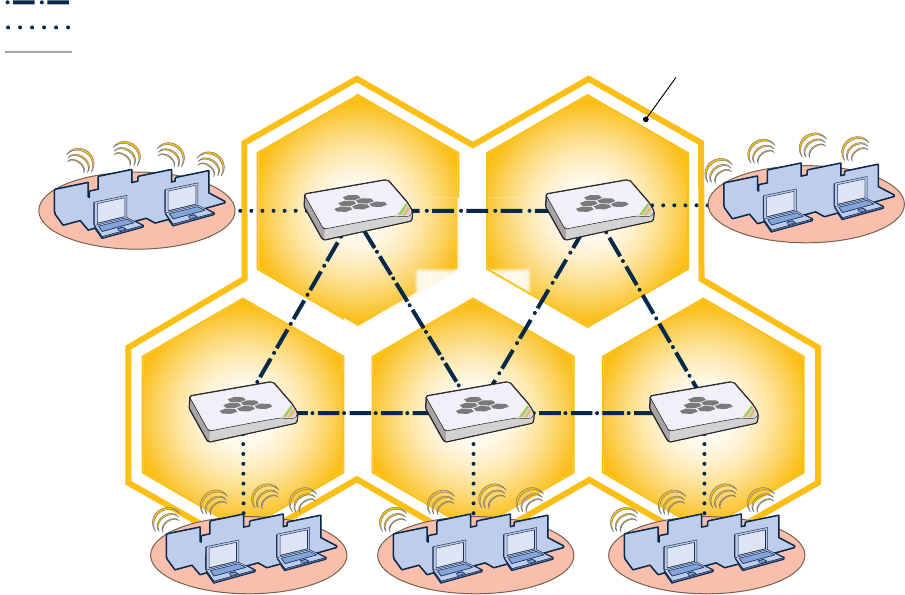
set of HiveAPs that exchange information with each other to form a collaborative whole (see Figure 1). Through
coordinated actions based on shared information, hive members can provide the following services that autonomous
APs cannot:
• Consistent QoS (quality of service) policy enforcement across all hive members
• Coordinated and predictive wireless access control that provides fast roaming to clients moving from one hive
member to another
• Best-path routing for optimized data forwarding
• Automatic radio frequency and power selection
Figure 1 HiveAPs in a Hive
Hive Members
Wired or Wireless Hive Communications (Backhaul)
Wireless Network Access Connections
Wired Ethernet Network Connections
Not shown: Switches for wired backhaul
connections and the portal link to the wired network.
Wireless Clients
Wireless Clients
Wireless Clients
Hive










