User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Getting Started
- 3 Utility Configuration
- 4 Web Interface
- 4.1 Overview
- 4.2 Accessing the Web Page
- 4.3 Overview
- 4.4 Network Settings
- 4.5 Wireless Settings
- 4.6 Alarm
- 4.7 Administration
- 5 Telnet/Serial Console Configuration
44 EKI-6233BN User Manual
4.4.3.2 DMZ
A Demilitarized Zone is used to provide Internet services without sacrificing
unauthorized access to its local private network. Typically, the DMZ host contains
devices accessible to the Internet traffic, such as Web (HTTP) servers, FTP servers,
SMTP (e-mail) servers and DNS servers.
To access this page, click Networking > Forwarding > DMZ.
Figure 4.13 Networking > Forwarding > DMZ
The following table describes the items in the previous figure.
4.4.4 Security
4.4.4.1 Filter
The firewall is a system or group of systems that enforce an access control policy
between two networks. It may also be defined as a mechanism used to protect a
trusted network from an un-trusted network. The device has capabilities of Source IP
Filtering, Destination IP Filtering, Source Port Filtering, Destination Port Filtering,
Port Forwarding as well as DMZ.
Source IP Filtering: The source IP filtering gives users the ability to restrict certain
types of data packets from users local network to Internet through the device. Use of
such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting users local network.
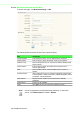
To access this page, click Networking Settings > Security > Filter.
Figure 4.14 Networking Settings > Security > Filter
Item Description
DMZ Click the radio button to enable or disable the DMZ function.
IP Enter the IP address to designate a static IP address as the DMZ
target.
Apply Click Apply to save the values and update the screen.
Item Description
Filter
Enabled Click the radio button to enable or disable the Filter policy.
Direction Click the drop-down menu to select the direction of the data packet
traffic for the entry: LAN to WAN, WAN to LAN.
Source IP Enter the IP address of the sender address.