User Manual
Appendix D RS-485 Network 55
D.1 Basic Network Layout
Multi-drop RS-485 implies that there are two main wires in a segment.
The connected systems tap from these two lines with so called drop
cables. Thus all connections are parallel and connecting or disconnect-
ing of a node doesn’t affect the network as a whole. Since ADAM-5000
systems use the RS-485 standard and an ASCII-based commands set,
they can connect and communicate with all ASCII-based computers and
terminals. The basic layouts that can be used for an RS-485 network are:
Daisychain
The last module of a segment is a repeater. It is directly connected to the
main-wires thereby ending the first segment and starting the next seg-
ment. Up to 32 addressable systems can be daisychained . This limitation
is a physical one. When using more systems per segment the IC driver
current rapidly decreases, causing communication errors. In total, the
network can hold up to 256 addressable systems. The limitation on this
number is the two-character hexadecimal address code that can address
256 combinations. The ADAM converter, ADAM repeaters and the host
computer are non addressable units and therefore are not included in
these numbers.
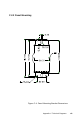
Figure D-1: Daisychaining
Coverter
RS232/RS485
RS-232
RS-485
Repeater
1
Setgment 2Setgment 1
1 2 N 1