User's Manual
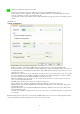
802.1x Setting
802.1x is a authentication for ?WPA?and ?WPA2?certificate to server.
- Authentication type:
i PEAP: Protect Extensible Authentication Protocol. PEAP transport securely authentication data by
using tunneling between PEAP clients and an authentication server. PEAP can authenticate wireless
LAN clients using only server-side certificates, thus simplifying the implementation and
administration of a secure wireless LAN.
ii TLS/Smart Card: Transport Layer Security. Provides for certificate-based and mutual authentication
of the client and the network. It relies on client-side and server-side certificates to perform
authentication and can be used to dynamically generate user-based and session-based WEP keys to
secure subsequent communications between the WLAN client and the access point.
iii TTLS: Tunneled Transport Layer Security. This security method provides for certificate-based,
mutual authentication of the client and network through an encrypted channel. Unlike EAP-TLS,
EAP-TTLS requires only server-side certificates.
iv LEAP: Light Extensible Authentication Protocol. It is an EAP authentication type used primarily in
Cisco Aironet WLANs. It encrypts data transmissions using dynamically generated WEP keys, and
supports mutual authentication.
v MD5-Challenge: Message Digest Challenge. Challenge is an EAP authentication type that provides
base-level EAP support. It provides for only one-way authentication - there is no mutual
authentication of wireless client and the network.
- Session Resumption: user can choose “ Disable ”, “ Reauthentication ”, “ Roaming ”, “ SameSsid ” and “
Always ”.
- Identity and Password: Identity and password for server.
- Use Client Certicate: Client Certicate for server authentication.
- Tunnel Authentication
Protocol: Tunnel protocol, List information include “ EAP-MSCHAP ”, “ EAP-MSCHAP v2 ”, “ CAHAP ”
and “ MD5 ”
Tunnel Identity: Identity for tunnel.
Tunnel Password: Password for tunnel.
- CA Server: Certificate Authority Server. Each certificate is signed or issued by it.
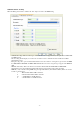
CA Server
Depending on the EAP in use, only the server or both the server and client may be authenticated and require a
certificate. Server certificates identify a server, usually an authentication or RADIUS server to clients. Most EAPs
require a certificate issued by a root authority or a trusted commercial CA. Show as the figure.
1. Certificate issuer: Choose use server that issuer of certificates.
- 6 -