Troubleshooting guide
Example Configurations
61200860L1-29.4E Copyright © 2012 ADTRAN, Inc. 43
Example 5: Load Sharing When Multihomed to Multiple ISPs
AOS allows multiple equal cost routes to be used for the purposes of load sharing outbound traffic.
The need for load sharing is typically found in BGP applications where an AOS device is multihoming
with multiple connections to different ISPs. The BGP protocol does not provide support for load sharing.
Therefore, BGP will always export the single best path for a given prefix to the IP route table. However,
there are methods that can be implemented that will allow multiple BGP-derived routes to be imported into
the IPv4 route table. Aside from the BGP-specific configuration, load sharing must be globally enabled on
the AOS device to allow the presence of multiple equal cost routes in the IP route table.
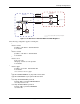
The following example illustrates load sharing across multiple links where the customer’s router is
multihomed to two different ISPs. Each ISP is advertising a default route to the AOS device. The default
routes contain equal BGP attributes, therefore one route is no more desirable than the other according to
the BGP selection process. The objective is to ensure that outbound traffic from the customer’s network is
load balanced (load shared) between the two Internet connections.
Several configuration steps are needed to allow BGP load sharing to take place. The ip load-sharing
per-destination command must be enabled in Global Configuration mode. This command allows
duplicate routes to exist in the routing table. The command maximum-paths 2 is issued in BGP
Configuration mode to allow up to two equal cost routes from BGP to be exported to the routing table. In
order for multiple BGP routes to the same destination to be candidates for load sharing, they must be equal
cost and share the same AS number in the AS path attribute. Since each ISP in this example owns their
own unique AS number that is added on to the BGP path attribute, an arbitrary AS number must be
prepended to each eBGP neighbor’s BGP advertisement. This AS number enables the BGP routes to
become candidates for load sharing since the routes now appear to originate from the same AS. This is
accomplished with the route map (LOAD-SHARE) applied inbound to each eBGP neighbor. It matches the
prefix list (DEFAULT) that only allows the default route, which automatically filters any other advertised
routes. The route map then prepends the same arbitrary AS path (65009) to the default route prefix learned
by each neighbor. The prefix list (PUBLIC-BLOCK) is used to advertise only the customer public block
Consult with the ISP to determine which BGP attributes they will honor when making a
decision on routing traffic back to your advertised AS.
The command clock source line is enabled by default. Therefore, this command will not
appear in the output when the show running-config command is issued.
The maximum number of equal cost routes supported in AOS is 6.
At the global level, load sharing has two different implementation options: per packet and
per destination. Refer to Configuring IP Load Sharing in AOS (ADTRAN’s Knowledge Base
article 1994) for more information on these load sharing options.