Operation Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1: Getting started
- Chapter 2: Digital audio fundamentals
- Chapter 3: Workflow and workspace
- Chapter 4: Setting up Adobe Audition
- Chapter 5: Importing, recording, and playing audio
- Chapter 6: Editing audio files
- Displaying audio in Edit View
- Selecting audio
- Copying, cutting, pasting, and deleting audio
- Visually fading and changing amplitude
- Working with markers
- Creating and deleting silence
- Inverting and reversing audio
- Generating audio
- Analyzing phase, frequency, and amplitude
- Converting sample types
- Recovery and undo
- Chapter 7: Applying effects
- Chapter 8: Effects reference
- Amplitude and compression effects
- Delay and echo effects
- Filter and equalizer effects
- Modulation effects
- Restoration effects
- Reverb effects
- Special effects
- Stereo imagery effects
- Changing stereo imagery
- Binaural Auto-Panner effect (Edit View only)
- Center Channel Extractor effect
- Channel Mixer effect
- Doppler Shifter effect (Edit View only)
- Graphic Panner effect
- Pan/Expand effect (Edit View only)
- Stereo Expander effect
- Stereo Field Rotate VST effect
- Stereo Field Rotate process effect (Edit View only)
- Time and pitch manipulation effects
- Multitrack effects
- Chapter 9: Mixing multitrack sessions
- Chapter 10: Composing with MIDI
- Chapter 11: Loops
- Chapter 12: Working with video
- Chapter 13: Creating surround sound
- Chapter 14: Saving and exporting
- Saving and exporting files
- Audio file formats
- About audio file formats
- 64-bit doubles (RAW) (.dbl)
- 8-bit signed (.sam)
- A/mu-Law Wave (.wav)
- ACM Waveform (.wav)
- Amiga IFF-8SVX (.iff, .svx)
- Apple AIFF (.aif, .snd)
- ASCII Text Data (.txt)
- Audition Loop (.cel)
- Creative Sound Blaster (.voc)
- Dialogic ADPCM (.vox)
- DiamondWare Digitized (.dwd)
- DVI/IMA ADPCM (.wav)
- Microsoft ADPCM (.wav)
- mp3PRO (.mp3)
- NeXT/Sun (.au, .snd)
- Ogg Vorbis (.ogg)
- SampleVision (.smp)
- Spectral Bitmap Image (.bmp)
- Windows Media Audio (.wma)
- Windows PCM (.wav, .bwf)
- PCM Raw Data (.pcm, .raw)
- Video file formats
- Adding file information
- Chapter 15: Automating tasks
- Chapter 16: Building audio CDs
- Chapter 17: Keyboard shortcuts
- Chapter 18: Digital audio glossary
- Index
ADOBE AUDITION 3.0
User Guide
261
Overwrite Existing Files Saves existing files with a new name.
Delete Source File If Converted OK Deletes source files after they are converted successfully.
Remove From Source List If Converted OK Removes file names from the source list after the files are converted
successfully.
Output Filename Template Specifies how files are renamed. By default, the first part of the file name remains the
same, and the extension changes to match the chosen output format.
Alternatively, you can type a different extension, and you can set up conditions for how files are renamed by using
question marks and asterisks:
• A question mark (?) signifies that a character doesn’t change.
• An asterisk (*) denotes the original file name or extension.
Here are some examples of how files can be renamed:
See also
“Batch process files” on page 260
Scripts
About scripts
In Edit View, scripts let you save a series of actions, such as copying data or applying an effect, so you can perform
those actions again with the click of a button. Scripts are simple text files that are similar to macros; Adobe Audition
stores the exact actions of your mouse and any tweaking of parameters, so you can repeat them in the same sequence
when you run the script.
For example, suppose you have a combination of effects with particular settings (an EQ setting, a Hall reverb, and so
on) that you want to apply often and in combination to achieve a certain sound. You can record these steps, along
with effect-specific settings, and then apply them at any time simply by running a script.
Adobe Audition lets you create three types of scripts:
• Scripts that start from scratch on a newly created waveform; their first command is File > New.
• Scripts that work on the currently open waveform, from the start-time indicator to the end of the file.
• Scripts that work on a selected range in an open waveform.
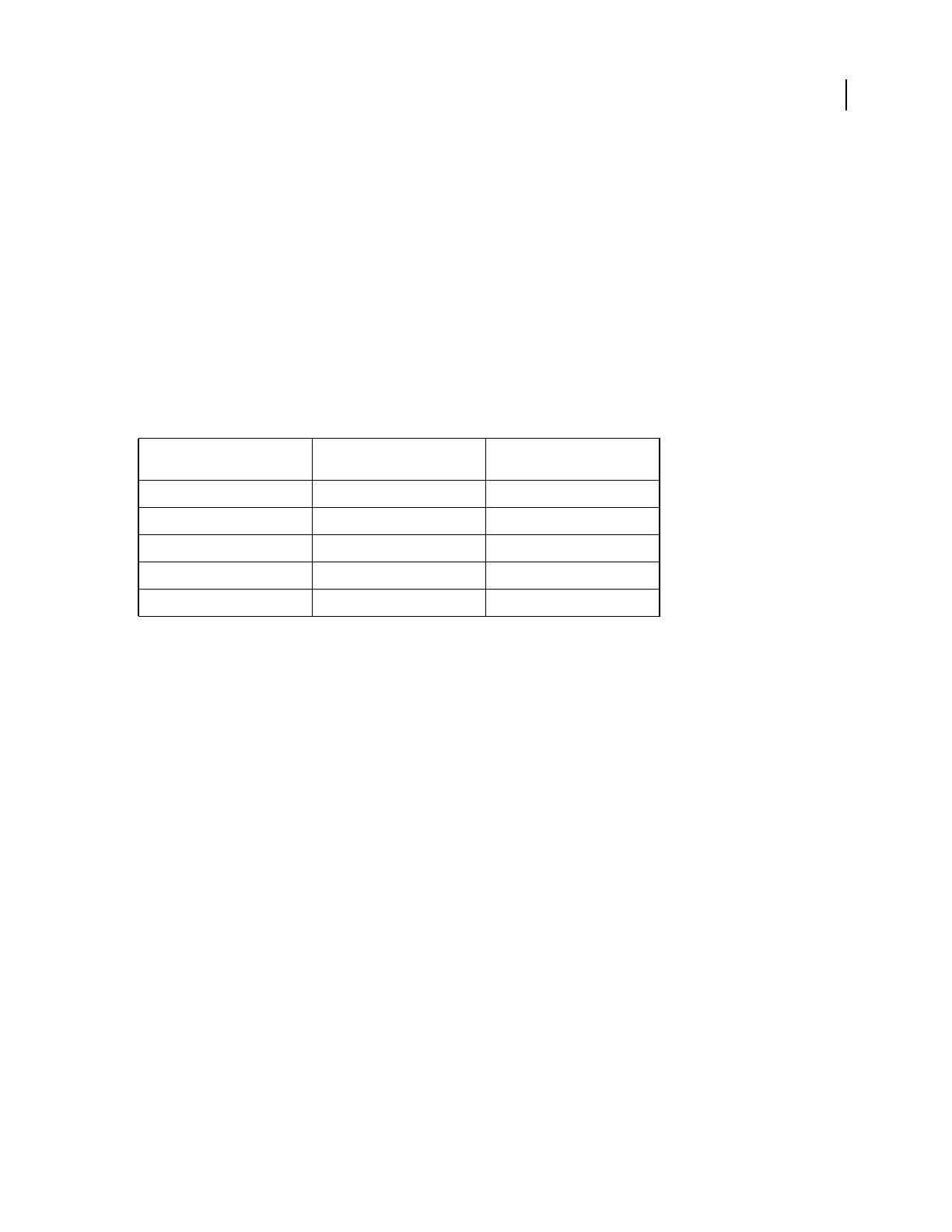
Original name Output Filename Template
name
Resulting file name
zippy.aif *.wav zippy.wav
toads.pcm q*.voc qtoads.voc
funny.mp3 b???????.* bunny.mp3
biglong.au ????.au bigl.au
bart.wav *x.wav bartx.wav










