Operation Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1: Getting started
- Chapter 2: Digital audio fundamentals
- Chapter 3: Workflow and workspace
- Chapter 4: Setting up Adobe Audition
- Chapter 5: Importing, recording, and playing audio
- Chapter 6: Editing audio files
- Displaying audio in Edit View
- Selecting audio
- Copying, cutting, pasting, and deleting audio
- Visually fading and changing amplitude
- Working with markers
- Creating and deleting silence
- Inverting and reversing audio
- Generating audio
- Analyzing phase, frequency, and amplitude
- Converting sample types
- Recovery and undo
- Chapter 7: Applying effects
- Chapter 8: Effects reference
- Amplitude and compression effects
- Delay and echo effects
- Filter and equalizer effects
- Modulation effects
- Restoration effects
- Reverb effects
- Special effects
- Stereo imagery effects
- Changing stereo imagery
- Binaural Auto-Panner effect (Edit View only)
- Center Channel Extractor effect
- Channel Mixer effect
- Doppler Shifter effect (Edit View only)
- Graphic Panner effect
- Pan/Expand effect (Edit View only)
- Stereo Expander effect
- Stereo Field Rotate VST effect
- Stereo Field Rotate process effect (Edit View only)
- Time and pitch manipulation effects
- Multitrack effects
- Chapter 9: Mixing multitrack sessions
- Chapter 10: Composing with MIDI
- Chapter 11: Loops
- Chapter 12: Working with video
- Chapter 13: Creating surround sound
- Chapter 14: Saving and exporting
- Saving and exporting files
- Audio file formats
- About audio file formats
- 64-bit doubles (RAW) (.dbl)
- 8-bit signed (.sam)
- A/mu-Law Wave (.wav)
- ACM Waveform (.wav)
- Amiga IFF-8SVX (.iff, .svx)
- Apple AIFF (.aif, .snd)
- ASCII Text Data (.txt)
- Audition Loop (.cel)
- Creative Sound Blaster (.voc)
- Dialogic ADPCM (.vox)
- DiamondWare Digitized (.dwd)
- DVI/IMA ADPCM (.wav)
- Microsoft ADPCM (.wav)
- mp3PRO (.mp3)
- NeXT/Sun (.au, .snd)
- Ogg Vorbis (.ogg)
- SampleVision (.smp)
- Spectral Bitmap Image (.bmp)
- Windows Media Audio (.wma)
- Windows PCM (.wav, .bwf)
- PCM Raw Data (.pcm, .raw)
- Video file formats
- Adding file information
- Chapter 15: Automating tasks
- Chapter 16: Building audio CDs
- Chapter 17: Keyboard shortcuts
- Chapter 18: Digital audio glossary
- Index
ADOBE AUDITION 3.0
User Guide
190
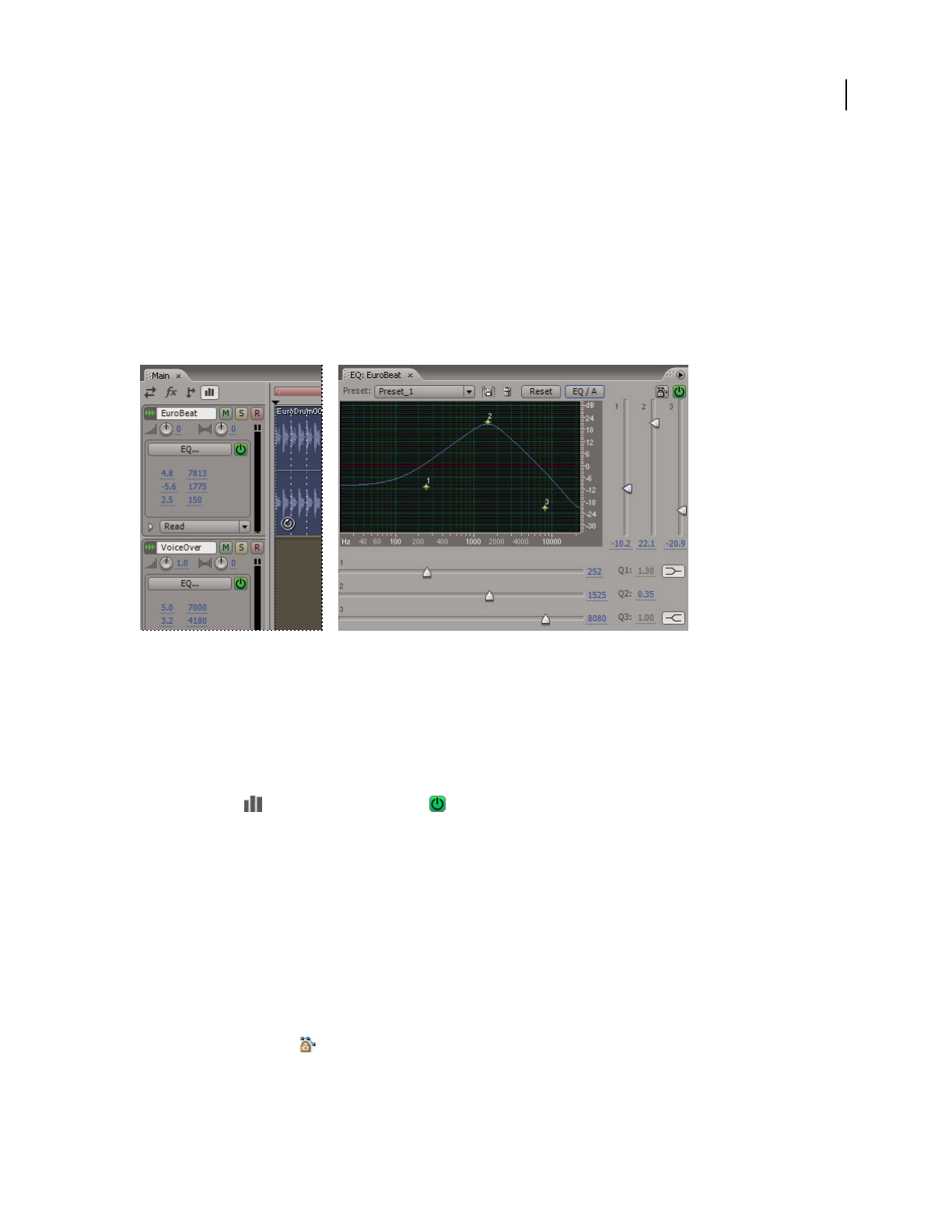
Equalizing tracks
For each track, Multitrack View provides a three-band parametric equalizer that you can access in the Main, Mixer,
or Track EQ panel. The Main and Mixer panels provide quick access to commonly used settings; the Track EQ panel
provides more precise and sophisticated controls.
In the EQ area of the Main panel and Mixer, the blue text shows the current equalization for three frequency bands.
You drag across this text to change center frequency and adjust boost or attenuation.
In the Track EQ panel, you use a graph to visually adjust equalization settings. In addition to options offered by the
Main panel and Mixer, the Track EQ panel provides access to presets, bandwidth controls, and other advanced
options.
Equalizing tracks
A. Numeric controls in the Main panel B. Graphical controls in the Track EQ panel
See also
“Use effect presets” on page 104
Equalize a track in the Main panel or Mixer
1
In the EQ area , click the EQ Power button .
2 Drag across the blue text for each band to specify boost or attenuation in decibels, and center frequency in Hertz.
3 (Optional) Click the EQ button to open the Track EQ panel and see a graphical view of your settings.
Equalize a track in the Track EQ panel
1
Select the track, and then choose Window > Track EQ.
2 Set the following options:
Preset options Let you store and apply identical settings to multiple tracks.
EQ/A-B Lets you compare two different equalization settings. For example, you can adjust settings for the EQ/A
bank, and then click the button to access the default, unequalized settings for the EQ/B bank.
Track EQ Safe During Write Protects all settings from inadvertent changes that can occur when recording
automation.
A B










