Operation Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1: Getting started
- Chapter 2: Digital audio fundamentals
- Chapter 3: Workflow and workspace
- Chapter 4: Setting up Adobe Audition
- Chapter 5: Importing, recording, and playing audio
- Chapter 6: Editing audio files
- Displaying audio in Edit View
- Selecting audio
- Copying, cutting, pasting, and deleting audio
- Visually fading and changing amplitude
- Working with markers
- Creating and deleting silence
- Inverting and reversing audio
- Generating audio
- Analyzing phase, frequency, and amplitude
- Converting sample types
- Recovery and undo
- Chapter 7: Applying effects
- Chapter 8: Effects reference
- Amplitude and compression effects
- Delay and echo effects
- Filter and equalizer effects
- Modulation effects
- Restoration effects
- Reverb effects
- Special effects
- Stereo imagery effects
- Changing stereo imagery
- Binaural Auto-Panner effect (Edit View only)
- Center Channel Extractor effect
- Channel Mixer effect
- Doppler Shifter effect (Edit View only)
- Graphic Panner effect
- Pan/Expand effect (Edit View only)
- Stereo Expander effect
- Stereo Field Rotate VST effect
- Stereo Field Rotate process effect (Edit View only)
- Time and pitch manipulation effects
- Multitrack effects
- Chapter 9: Mixing multitrack sessions
- Chapter 10: Composing with MIDI
- Chapter 11: Loops
- Chapter 12: Working with video
- Chapter 13: Creating surround sound
- Chapter 14: Saving and exporting
- Saving and exporting files
- Audio file formats
- About audio file formats
- 64-bit doubles (RAW) (.dbl)
- 8-bit signed (.sam)
- A/mu-Law Wave (.wav)
- ACM Waveform (.wav)
- Amiga IFF-8SVX (.iff, .svx)
- Apple AIFF (.aif, .snd)
- ASCII Text Data (.txt)
- Audition Loop (.cel)
- Creative Sound Blaster (.voc)
- Dialogic ADPCM (.vox)
- DiamondWare Digitized (.dwd)
- DVI/IMA ADPCM (.wav)
- Microsoft ADPCM (.wav)
- mp3PRO (.mp3)
- NeXT/Sun (.au, .snd)
- Ogg Vorbis (.ogg)
- SampleVision (.smp)
- Spectral Bitmap Image (.bmp)
- Windows Media Audio (.wma)
- Windows PCM (.wav, .bwf)
- PCM Raw Data (.pcm, .raw)
- Video file formats
- Adding file information
- Chapter 15: Automating tasks
- Chapter 16: Building audio CDs
- Chapter 17: Keyboard shortcuts
- Chapter 18: Digital audio glossary
- Index
ADOBE AUDITION 3.0
User Guide
11
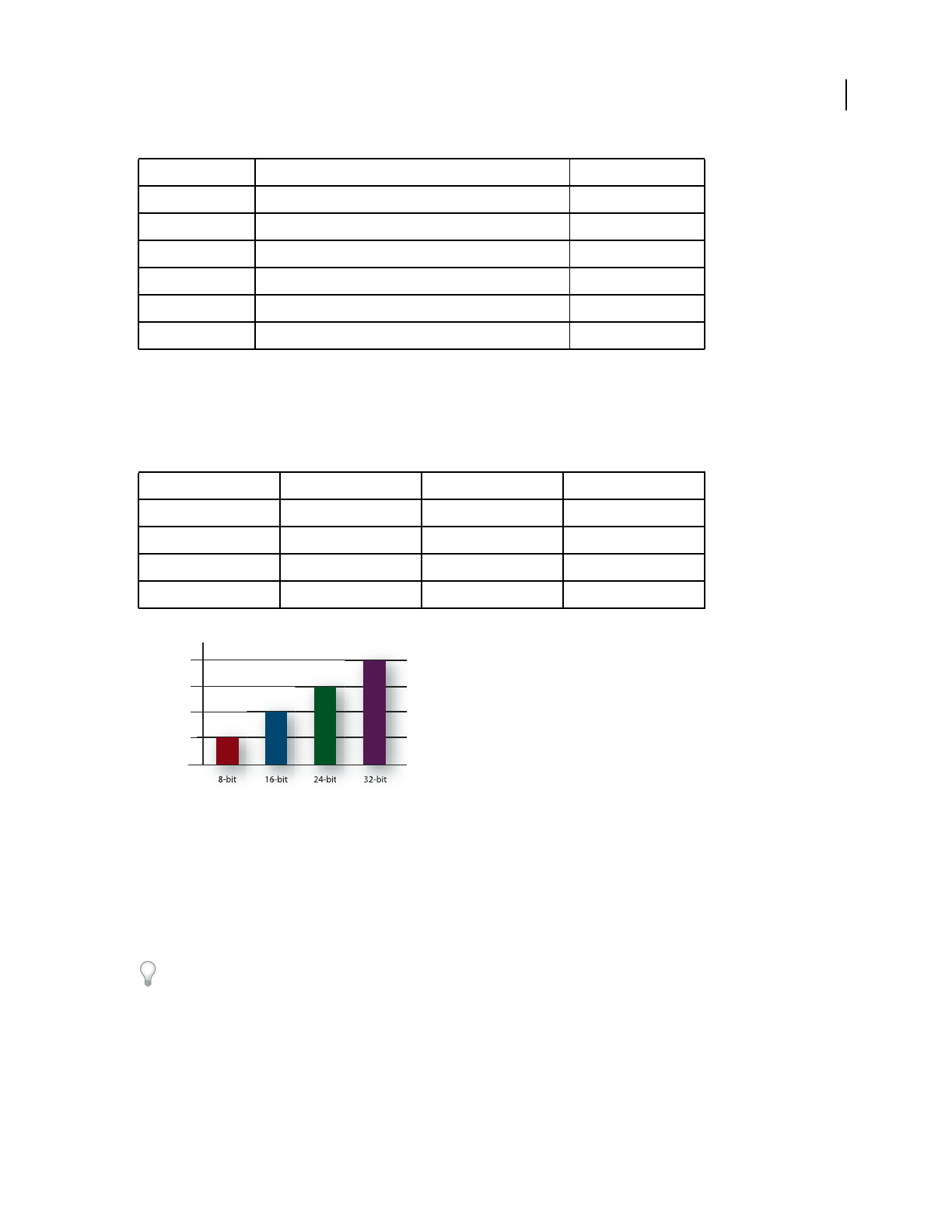
Bit depth
Just as sample rate determines frequency range, bit depth determines dynamic range. When a sound wave is sampled,
each sample is assigned the amplitude value closest to the original wave’s amplitude. Higher bit depth provides more
possible amplitude values, producing greater dynamic range, a lower noise floor, and higher fidelity:
Higher bit depths provide greater dynamic range.
Audio file contents and size
An audio file on your hard drive, such as a WAV file, consists of a small header indicating sample rate and bit depth,
and then a long series of numbers, one for each sample. These files can be very large. For example, at 44,100 samples
per second and 16 bits per sample, a file requires 86 KB per second—about 5 MB per minute. That figure doubles to
10 MB per minute for a stereo CD, which has two channels.
In contrast to a digital audio file, a MIDI file might be as small as 10 KB per minute, so you can store up to 100
minutes of MIDI per megabyte. For more information, see “Understanding MIDI data and VST instruments” on
page 213.
Sample rate Quality level Frequency range
11,025 Hz Poor AM radio (low-end multimedia) 0–5,512 Hz
22,050 Hz Near FM radio (high-end multimedia) 0–11,025 Hz
32,000 Hz Better than FM radio (standard broadcast rate) 0–16,000 Hz
44,100 Hz CD 0–22,050 Hz
48,000 Hz Standard DVD 0–24,000 Hz
96,000 Hz High-end DVD 0–48,000 Hz
Bit depth Quality level Amplitude values Dynamic range
8-bit Telephony 256 48 dB
16-bit CD 65,536 96 dB
24-bit DVD 16,777,216 144 dB
32-bit Best 4,294,967,296 192 dB
192 dB
144 dB
48 dB
0 dB
96 dB
8-bit
16-bit 24-bit 32-bit