Operation Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1: Getting started
- Chapter 2: Digital audio fundamentals
- Chapter 3: Workflow and workspace
- Chapter 4: Setting up Adobe Audition
- Chapter 5: Importing, recording, and playing audio
- Chapter 6: Editing audio files
- Displaying audio in Edit View
- Selecting audio
- Copying, cutting, pasting, and deleting audio
- Visually fading and changing amplitude
- Working with markers
- Creating and deleting silence
- Inverting and reversing audio
- Generating audio
- Analyzing phase, frequency, and amplitude
- Converting sample types
- Recovery and undo
- Chapter 7: Applying effects
- Chapter 8: Effects reference
- Amplitude and compression effects
- Delay and echo effects
- Filter and equalizer effects
- Modulation effects
- Restoration effects
- Reverb effects
- Special effects
- Stereo imagery effects
- Changing stereo imagery
- Binaural Auto-Panner effect (Edit View only)
- Center Channel Extractor effect
- Channel Mixer effect
- Doppler Shifter effect (Edit View only)
- Graphic Panner effect
- Pan/Expand effect (Edit View only)
- Stereo Expander effect
- Stereo Field Rotate VST effect
- Stereo Field Rotate process effect (Edit View only)
- Time and pitch manipulation effects
- Multitrack effects
- Chapter 9: Mixing multitrack sessions
- Chapter 10: Composing with MIDI
- Chapter 11: Loops
- Chapter 12: Working with video
- Chapter 13: Creating surround sound
- Chapter 14: Saving and exporting
- Saving and exporting files
- Audio file formats
- About audio file formats
- 64-bit doubles (RAW) (.dbl)
- 8-bit signed (.sam)
- A/mu-Law Wave (.wav)
- ACM Waveform (.wav)
- Amiga IFF-8SVX (.iff, .svx)
- Apple AIFF (.aif, .snd)
- ASCII Text Data (.txt)
- Audition Loop (.cel)
- Creative Sound Blaster (.voc)
- Dialogic ADPCM (.vox)
- DiamondWare Digitized (.dwd)
- DVI/IMA ADPCM (.wav)
- Microsoft ADPCM (.wav)
- mp3PRO (.mp3)
- NeXT/Sun (.au, .snd)
- Ogg Vorbis (.ogg)
- SampleVision (.smp)
- Spectral Bitmap Image (.bmp)
- Windows Media Audio (.wma)
- Windows PCM (.wav, .bwf)
- PCM Raw Data (.pcm, .raw)
- Video file formats
- Adding file information
- Chapter 15: Automating tasks
- Chapter 16: Building audio CDs
- Chapter 17: Keyboard shortcuts
- Chapter 18: Digital audio glossary
- Index
ADOBE AUDITION 3.0
User Guide
150
To achieve the best results with the Noise Reduction effect, apply it to 16- or 32-bit audio with no DC offset. With
8-bit audio, this effect cannot reduce noise below -45 dB, which is very audible. (To achieve a lower noise floor with
8-bit audio, upsample the file to 16 bits, apply the Noise Reduction effect, and downsample the file back to 8 bits.)
With a DC offset, this effect may introduce clicks in quiet passages. (To remove a DC offset, select the Center Wave
preset provided by the Amplify/Fade effect.)
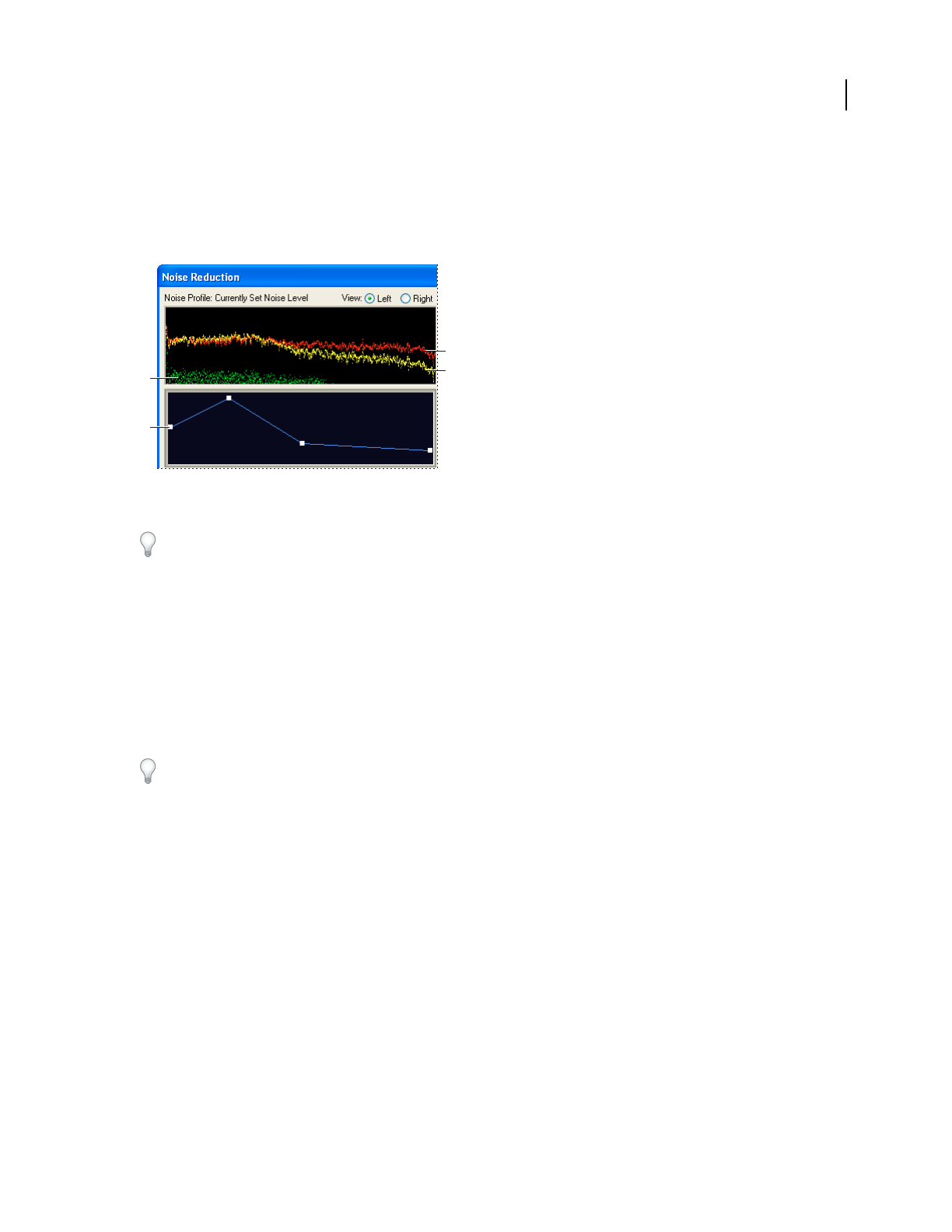
Adjusting frequency-specific settings with the Noise Reduction graphs
A. Noise floor B. Reduction graph C. Original audio D. Processed audio
To reduce noise added by a sound card during recording, start the recording with a second of silence. After recording
iscomplete,usethatsilenceastheNoiseReductionProfile,andthenremoveitfromthecompleterecording.Insome
cases, this process can increase dynamic range by 10 dB.
See also
“About process effects” on page 104
“Control effects settings with graphs” on page 104
Apply the Noise Reduction effect
1
In Edit View, select a range that contains only noise and is at least half a second long.
To select noise in a specific frequency range, use the Marquee Selection tool. (See “Select spectral ranges” on page 73.)
2 Choose Effects > Restoration > Capture Noise Reduction Profile.
3 In the Main panel, select the range from which you want to remove noise.
4 Choose Effects > Restoration > Noise Reduction.
5 Set the desired options.
Noise Reduction options
View Displays either the left or right channel noise profile. The amount of noise reduction is always the same for
both channels. To perform separate levels of reduction on each channel, edit the channels individually.
Noise Profile graph Represents, in yellow, the amount of noise reduction that will occur at any particular frequency.
Adjust the graph by moving the Noise Reduction Level slider.
Capture Profile Extracts a noise profile from a selected range, indicating only background noise. Adobe Audition
gathers statistical information about the background noise so it can remove it from the remainder of the waveform.
A
B
C
D










