Operation Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Chapter 1: Getting started
- Chapter 2: Digital audio fundamentals
- Chapter 3: Workflow and workspace
- Chapter 4: Setting up Adobe Audition
- Chapter 5: Importing, recording, and playing audio
- Chapter 6: Editing audio files
- Displaying audio in Edit View
- Selecting audio
- Copying, cutting, pasting, and deleting audio
- Visually fading and changing amplitude
- Working with markers
- Creating and deleting silence
- Inverting and reversing audio
- Generating audio
- Analyzing phase, frequency, and amplitude
- Converting sample types
- Recovery and undo
- Chapter 7: Applying effects
- Chapter 8: Effects reference
- Amplitude and compression effects
- Delay and echo effects
- Filter and equalizer effects
- Modulation effects
- Restoration effects
- Reverb effects
- Special effects
- Stereo imagery effects
- Changing stereo imagery
- Binaural Auto-Panner effect (Edit View only)
- Center Channel Extractor effect
- Channel Mixer effect
- Doppler Shifter effect (Edit View only)
- Graphic Panner effect
- Pan/Expand effect (Edit View only)
- Stereo Expander effect
- Stereo Field Rotate VST effect
- Stereo Field Rotate process effect (Edit View only)
- Time and pitch manipulation effects
- Multitrack effects
- Chapter 9: Mixing multitrack sessions
- Chapter 10: Composing with MIDI
- Chapter 11: Loops
- Chapter 12: Working with video
- Chapter 13: Creating surround sound
- Chapter 14: Saving and exporting
- Saving and exporting files
- Audio file formats
- About audio file formats
- 64-bit doubles (RAW) (.dbl)
- 8-bit signed (.sam)
- A/mu-Law Wave (.wav)
- ACM Waveform (.wav)
- Amiga IFF-8SVX (.iff, .svx)
- Apple AIFF (.aif, .snd)
- ASCII Text Data (.txt)
- Audition Loop (.cel)
- Creative Sound Blaster (.voc)
- Dialogic ADPCM (.vox)
- DiamondWare Digitized (.dwd)
- DVI/IMA ADPCM (.wav)
- Microsoft ADPCM (.wav)
- mp3PRO (.mp3)
- NeXT/Sun (.au, .snd)
- Ogg Vorbis (.ogg)
- SampleVision (.smp)
- Spectral Bitmap Image (.bmp)
- Windows Media Audio (.wma)
- Windows PCM (.wav, .bwf)
- PCM Raw Data (.pcm, .raw)
- Video file formats
- Adding file information
- Chapter 15: Automating tasks
- Chapter 16: Building audio CDs
- Chapter 17: Keyboard shortcuts
- Chapter 18: Digital audio glossary
- Index
ADOBE AUDITION 3.0
User Guide
128
When designing a reverb, cut some of the high frequencies to simulate their absorption by surrounding walls. In
addition, when echoing, frequencies generally aren’t boosted. However, you can create interesting effects by entering
positive values. Boosting a Low Cut Filter while reducing the feedback setting is identical to reducing a High Cut Filter
and increasing the feedback setting.
Channels menu Providesthefollowingoptionsforusewithstereosourceaudio.Tospreadouttheeffectinthestereo
domain, at least one delay unit in the group should be cross-channel or single-channel:
• Left Only Adds delay to only the left channel.
• Right Only Adds delay to only the right channel.
• Discrete Stereo Adds delay to both channels.
• Stereo Swap Maps the delay for the left channel to the right channel and vice-versa.
• From Right To Left Delays audio from the right channel and adds it to the left channel.
• From Left To Right Delays audio from the left channel and adds it to the right channel.
• From Center To Surround Delays audio common to both channels and inverts phase of the left-channel delay
relative to the right-channel delay.
Filter and equalizer effects
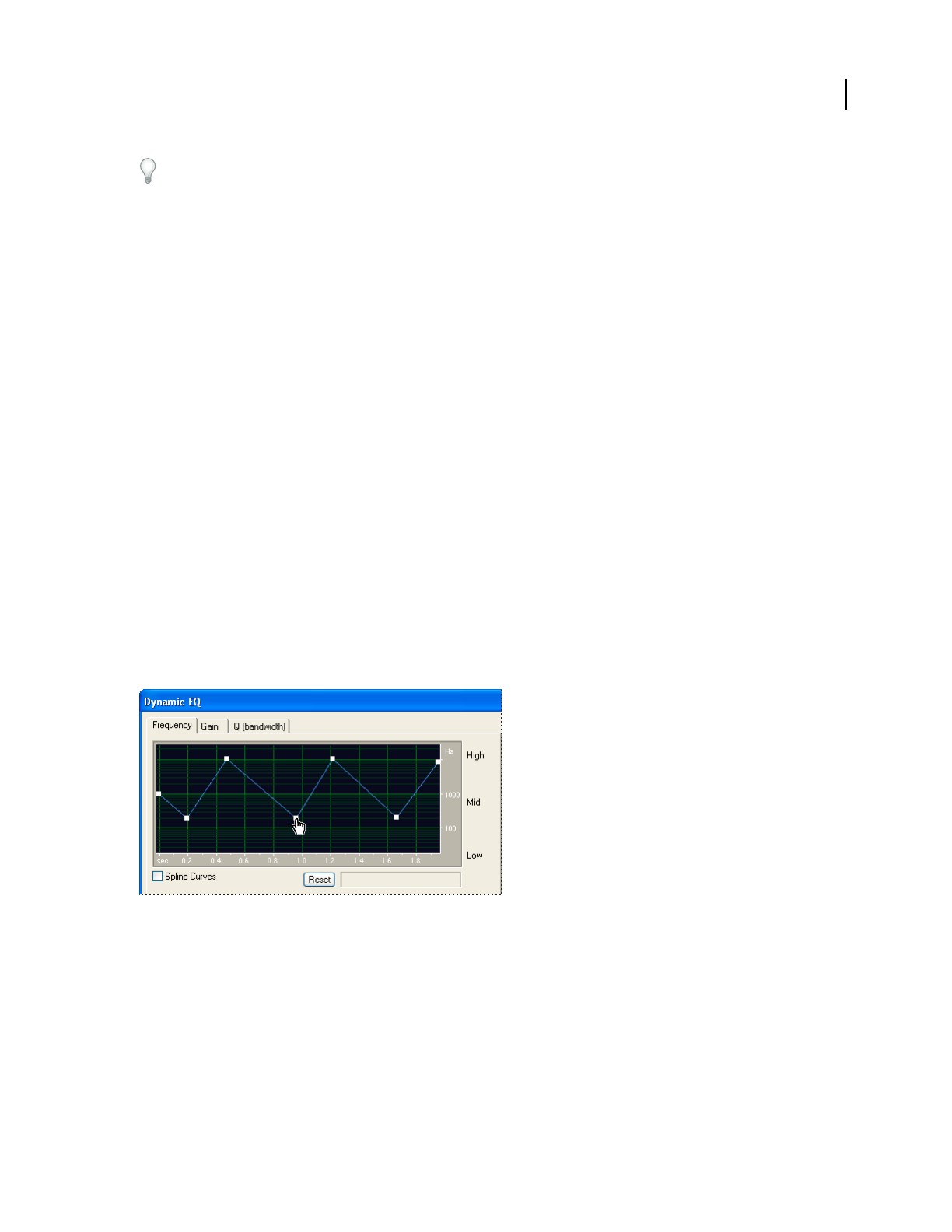
Dynamic EQ effect (Edit View only)
The Filter And EQ > Dynamic EQ effect varies the amount of equalization over time. For example, during the first
half of a waveform, you can boost high frequencies; during the second half, you can change the bandwidth of affected
frequencies. The Dynamic EQ dialog box provides three areas of controls: Gain, Frequency, and Q (bandwidth).
Frequency graph of Dynamic EQ effect (Rhythmic Sweep preset)
See also
“About process effects” on page 104
“Apply individual effects in Edit View” on page 107
“Control effects settings with graphs” on page 104
“Use effect presets” on page 104
“Add preroll and postroll to effects previews” on page 107










