User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- SECTION 1 General Information
- SECTION 2 InterReach™ Unison System Description
- SECTION 3 Unison Main Hub
- SECTION 4 Unison Expansion Hub
- SECTION 5 Unison Remote Access Unit
- SECTION 6 Installing Unison Components
- 6.1 Installation Requirements
- 6.2 Safety Precautions
- 6.3 Preparing for System Installation
- 6.4 Unison Component Installation Procedures
- 6.5 Starting and Configuring the System
- 6.6 Interfacing a Main Hub to a Base Station or Roof-top Antenna
- 6.7 Connecting Contact Alarms to a Unison System
- SECTION 7 Installing and Using the AdminManager Software
- SECTION 8 Designing a Unison Solution
- 8.1 Maximum Output Power per Carrier at RAU
- 8.2 Estimating RF Coverage
- 8.3 System Gain
- 8.4 Link Budget Analysis
- 8.4.1 Elements of a Link Budget for Narrowband Standards
- 8.4.2 Narrowband Link Budget Analysis for a Microcell Application
- 8.4.3 Elements of a Link Budget for CDMA Standards
- 8.4.4 Spread Spectrum Link Budget Analysis for a Microcell Application
- 8.4.5 Considerations for Re-Radiation (over-the-air) Systems
- 8.5 Optical Power Budget
- 8.6 Connecting a Main Hub to a Base Station
- 8.7 Designing for a Neutral Host System
- SECTION 9 Replacing Unison Components in an Operating System
- SECTION 10 Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Technical Assistance
- APPENDIX A Cables and Connectors
- APPENDIX B Compliance
- APPENDIX C Glossary
PN 8700-10 Help Hot Line (U.S. only): 1-800-530-9960 7-29
620003-0
PRELIMINARY Options when Connected Locally
Using the 10 dB Attenuation Setting
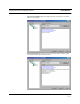
By selecting the Uplink and Downlink checkbox in the Advanced RAU Settings dia-
log box, the uplink and downlink signals in the individual RAU, which you specified
in the RAU Selection dialog box, are both reduced by 10 dB. One reason you may
want to use this setting is to reduce the RAU’s output power when an RAU is located
near an exterior wall of a building and its RF signal is going beyond the wall to the
outside of the building, where it can negatively affect the outdoor macro system.
The following table shows some examples of how the 10 dB attenuation setting
affects coverage distance. These examples assume a 0 dB gain system, a 3 dBi gain
antenna, and the difference between a –85 dB and a –75 dB design.
You can use the following formula to calculate the reduction in distance covered.
•d
orig
= original distance
•d
new
= new distance with 10 dB attenuation enabled
• PLS = path loss slope [dB]
d
new
= (10
–10/PLS
)d
orig
Examples:
d
new
= 0.31 d
orig
for PLS = 20 dB (free space)
d
new
= 0.46 d
orig
for PLS = 30 dB
Frequency Environment Reduction in Coverage Distance
800 MHz Open, like a parking garage 24 meters (80 feet)
800 MHz Heavily walled, like a Hospital 12.5 meters (41 feet)
1900 MHz Open, like a parking garage 24 meters (80 feet)
1900 MHz Heavily walled, like a Hospital 9 meters (30 feet)