User Manual
Table Of Contents
- VUE Key Layout
- VUE Soft keys
- Single Axis VUE Tool, and Datum keys
- Readout Parameter Access Code
- Access to Machine Parameter Operations
- Introduction
- Software Version
- VUE
- Symbols within Notes
- VUE Fonts
- Warranty
- Warranty Information:
- I – 1 Fundamentals of Positioning
- Datums
- Actual Position, Nominal Position, and Distance-To-Go
- Absolute Workpiece Positions
- Incremental workpiece positions
- Zero Angle Reference Axis
- Reading head position
- Encoder Reference Marks
- I – 2 General Operations for VUE
- Screen Layout
- VUE Hard Keys
- Power Up
- Reference Mark Evaluation
- Working without reference mark evaluation
- ENABLE/DISABLE REF function
- Operating Modes
- Setup
- Job Setup Parameters
- Units
- Scale Factor
- Mirror
- Diameter Axes
- Near Zero Warning
- Status Bar Settings
- Job Clock
- Console Adjustment
- Language
- Import/Export
- Set/Zero Soft Key
- I – 3 Milling Specific Operations
- Key Functions Detailed
- Tool Hard Key
- Tool Table
- Import/Export
- Tool Radius Compensation feature
- Sign for the length difference DL
- Calling the Tool from the Tool Table
- Datum Setting
- Datum Setting with a Tool
- Presets
- Absolute Distance Preset
- Preparation:
- Incremental Distance Preset
- 1/2 Hard Key
- Circle, and Linear Pattern
- Functions for milling pattern soft keys
- Circle pattern
- Linear Pattern
- Incline & Arc Milling
- Incline Milling
- Arc Milling
- I – 4 Turning Specific Operations
- Key Functions Detailed
- Tool Table
- Tool Display Icon
- Setting Tool Offsets with Tool/Set
- Import/Export
- Setting Tool Offsets with Lock Axis Function
- Calling a Tool from the Tool Table
- Datum Setting
- Setting Datums using LOCK AXIS Function
- Taper Calculator Hard Key
- Presets
- Radius/Diameter Soft Key
- Vectoring
- Coupling
- Z Coupling (turning applications only)
- Enabling Z Coupling
- Disabling Z Coupling
- II – 1 Installation Setup
- Installation Setup Parameters
- Exporting the current Installation Setup:
- Importing a new Tool Table
- Encoder Setup
- Display Configuration
- Error Compensation
- Linear Error Compensation
- Non-Linear Error Compensation
- Starting a Non-linear Error Compensation Table
- Configuring the Compensation Table
- Reading the Graph
- Viewing the Compensation Table
- Exporting the Current Compensation Table
- Importing a New Compensation Table
- Backlash Compensation
- Counter Settings
- Diagnostics
- Keypad Test
- Display Test
- II – 2 Installation and Electrical Connections
- Installation
- Electrical requirements
- Environmental
- Preventative maintenance
- II – 3 Dimensions
- Overview
- Accessory ID Number
4 I
I – 1 Fundamentals of Positioning
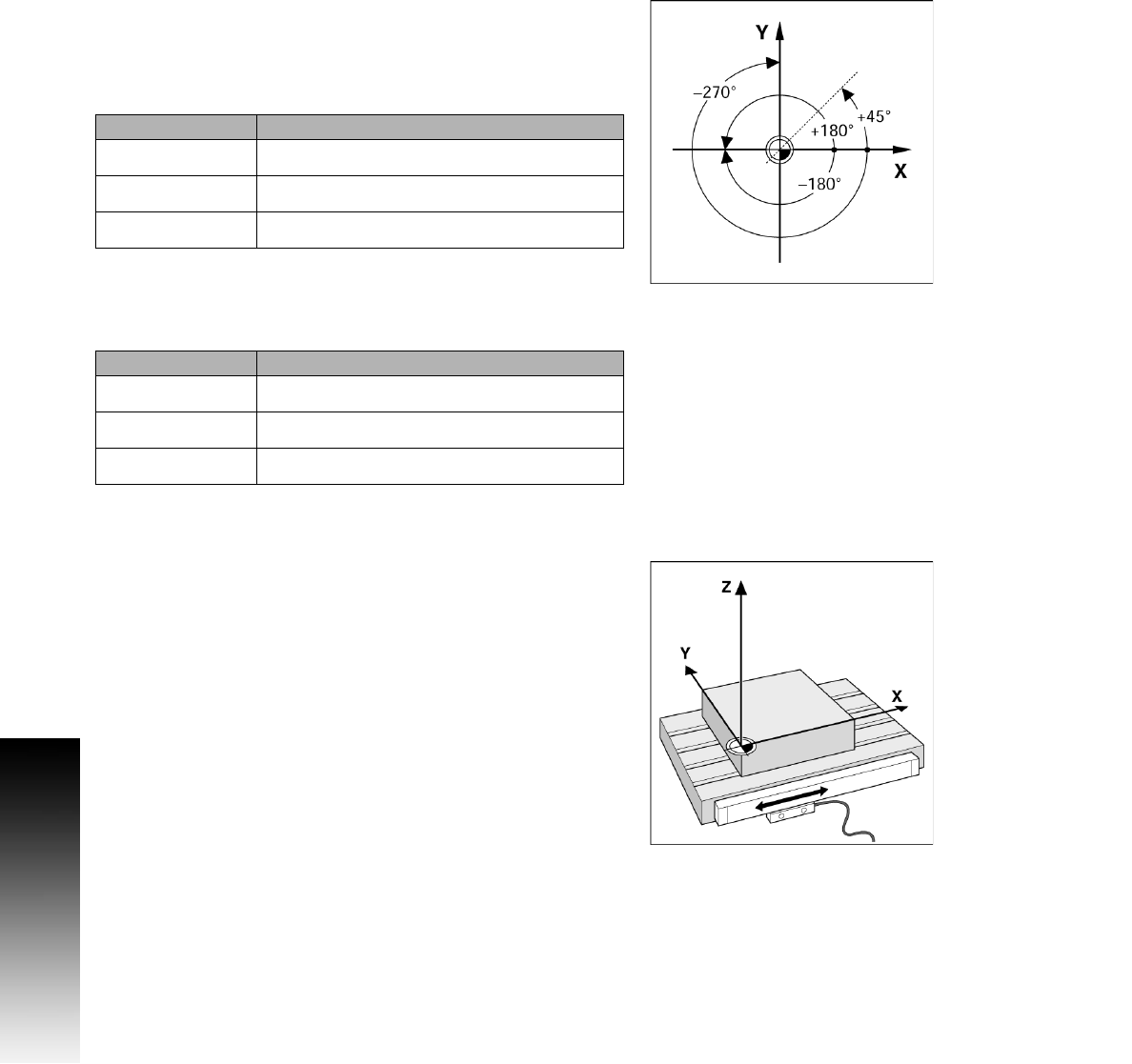
Zero Angle Reference Axis
The Zero Angle Reference Axis is the 0.0° position. It is defined as one
of the two axes in the plane of rotation. The following table defines the
Zero Angle where the position of the angle is zero for the three
possible planes of rotation.
For angular positions, the following reference axes are defined:
Positive direction of rotation is counterclockwise if the working plane
is viewed in the negative tool axis direction.
EXAMPLE: Angle in the working plane X / Y
Reading head position
The reading head position provides feed back to the VUE that converts
the movement of the machine axes into electrical signals. The VUE
constantly evaluates these signals, and calculates the actual positions
of the machine axes, which it displays as a numerical value on
the screen.
If there is an interruption in power, the calculated position will no
longer correspond to the actual position. When power is restored, you
can re-establish this relationship by using the reference marks on the
provided on the scale. The VUE provides the Reference Mark
Evaluation feature (REF).
Plane Zero Angle Reference Axis
XY +X
YZ +Y
ZX +Z
Plane Zero Angle Reference Axis
+ 45° ... bisecting line between +X and +Y
+/- 180° ... negative X axis
- 270° ... positive Y axis










