User guide
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introducing Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 What's new in Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 1.3 What you can do with Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 1.3.1 Taking an image of the master system
- 1.3.2 Deployment to specific machines (immediate, manual, and scheduled deployment)
- 1.3.3 Deployment to any ready machines (event-driven deployment)
- 1.3.4 Stand-alone deployment
- 1.3.5 Deployment with individual deployment settings
- 1.3.6 User-initiated deployment (custom deployment)
- 1.3.7 Deployment of a disk volume and MBR
- 1.3.8 Command-line mode and scripting under WinPE
- 1.4 Features of Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 1.4.1 List of machines
- 1.4.2 List of deployment tasks
- 1.4.3 Per-deployment licensing
- 1.4.4 Support for the VHD format
- 1.4.5 Graphical user interface in WinPE
- 1.4.6 E-mail notifications about deployment
- 1.4.7 Compatibility with images created by other Acronis products
- 1.4.8 Support for multiple network adapters
- 1.4.9 Multicast TTL and network bandwidth throttling
- 1.4.10 Falling back to unicast
- 1.4.11 Encrypted communication
- 1.4.12 Password protection
- 1.5 Supported operating systems for imaging and deployment
- 1.6 Licensing policy
- 1.7 Upgrading to Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 1.8 Technical Support
- 2 Understanding Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 3 Getting started with Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 4 Installation of Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 4.1 Supported operating systems
- 4.2 System requirements
- 4.3 Used ports and IP addresses
- 4.4 Typical installation
- 4.5 Custom installation
- 4.5.1 Installation procedure
- 4.5.2 Common installation configurations
- 4.5.3 Installation of components
- 4.5.3.1 Installation of Acronis Snap Deploy 5 Management Console
- 4.5.3.2 Installation of Acronis Snap Deploy 5 License Server
- 4.5.3.3 Installation of Acronis Snap Deploy 5 OS Deploy Server
- 4.5.3.4 Installation of Acronis PXE Server
- 4.5.3.5 Installation of Acronis Wake-on-LAN Proxy
- 4.5.3.6 Installation of Acronis Snap Deploy 5 Management Agent
- 4.6 Other ways of installation
- 4.7 Upgrading Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 4.8 Uninstalling Acronis Snap Deploy 5
- 5 Using Acronis Snap Deploy 5 Management Console
- 6 Using Acronis Snap Deploy 5 License Server
- 7 Deployment tools
- 8 Creating a master image
- 9 Validating a master image
- 10 Deploying a master image
- 10.1 Files supported as master images
- 10.2 Licenses for deployment
- 10.3 Deployment templates
- 10.4 Deployment through a deployment task
- 10.5 Stand-alone deployment
- 10.6 User-initiated deployment (custom deployment)
- 10.7 Deploying BIOS-based systems to UEFI-based and vice versa
- 11 Managing the list of machines (the Machines view)
- 12 Individual deployment settings
- 13 Managing deployment tasks (the Deployment tasks view)
- 14 Command-line mode and scripting under WinPE
- 15 Collecting system information
124 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2014
64-bit versions of all Windows Server operating systems starting with Windows Server 2008
x64 SP1 are convertible.
All other operating systems are non-convertible.
Source and target disk partition style: MBR or GPT. System and boot volumes of BIOS platforms
use MBR disks. System and boot volumes of UEFI platforms use GPT disks.
When selecting a non-initialized target disk for deployment, this disk will be automatically
initialized either to GPT or to MBR depending on the original disk partitioning style, the current
boot mode (UEFI or BIOS) and the type of operating systems (convertible or non-convertible)
that are located on this volume.
If the initialization may result in bootability loss, the software takes the partitioning style from
the source volume ignoring the target disk size. In such cases, the software can select the MBR
partitioning style for disks whose size is more than 2 TB; however, the disk space beyond 2 TB
will not be available for use.
If required, you can initialize the target disk manually by using a third-party partitioning tool,
such as Microsoft Disk Management or Acronis Disk Director.
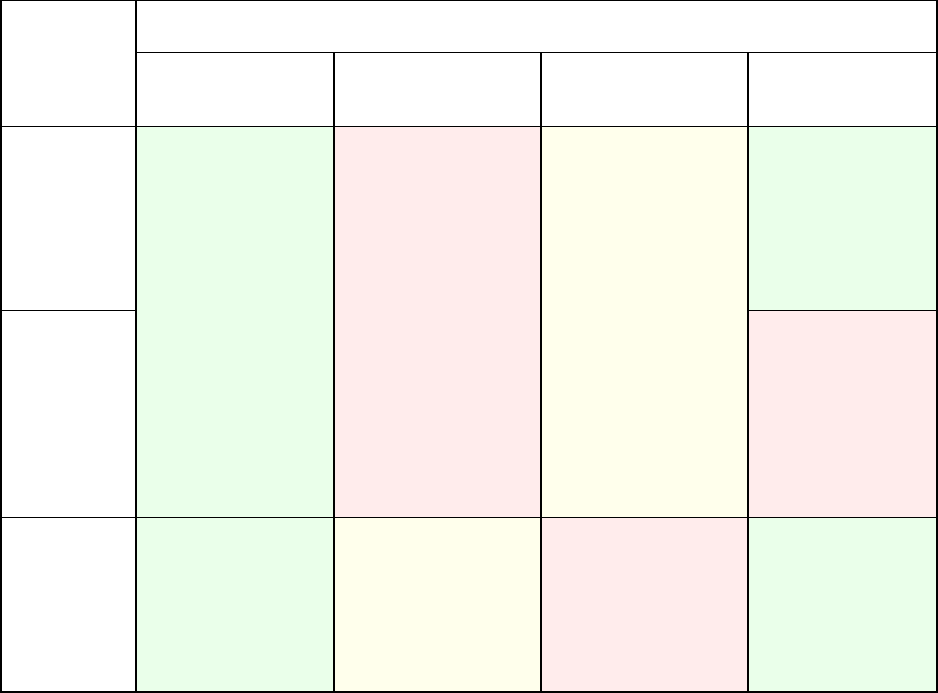
The following table summarizes whether it is possible to retain the system bootability when
deploying boot and system volumes of a BIOS-based system to UEFI-based and back.
A green background means that the system will be bootable. No user action is required.
A yellow background means that you need to perform additional steps to make the system
bootable. These steps are not possible on some machines.
A red background means that the system will not be able to boot due to BIOS and UEFI platform
limitations.
Original
system
Target hardware
BIOS
Disk: MBR
BIOS
Disk: GPT
UEFI
Disk: MBR
UEFI
Disk: GPT
BIOS
OS:
convertible
Solution
Deploy the operating
system to an MBR disk
or to an uninitialized
disk.
The target machine
must support BIOS.
Additional steps
1. Before deployment,
turn off the UEFI
mode in BIOS
2. Perform the
deployment under
the bootable media.
or
After deployment, turn
off the UEFI mode in
BIOS.
The convertible OS
will be automatically
converted to support
UEFI booting.
BIOS
OS: non-
convertible
Solution
Deploy the operating
system to an MBR
disk or to an
uninitialized disk.
UEFI
OS:
convertible
The convertible OS
will be automatically
converted to support
BIOS booting.
The target machine
must support UEFI.
Additional steps
1. Before deployment,
turn on the UEFI
Solution
Deploy the operating
system to a GPT disk or
to an uninitialized disk.