- LG Software Innovations Coffeemaker User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Revision history
- Contents
- About this guide
- Description
- System requirements
- List of ITG ISDN components
- Ordering rules and guidelines
- ITG ISL Trunk card description
- ITG ISL Trunk card physical description
- ISDN Signaling Link
- Dialing plans
- Quality of Service
- Fallback to alternate facilities
- Type of Service
- Fax support
- Remote Access
- Per-call statistics support using RADIUS Client
- SNMP MIB
- Codec profiles
- Security passwords
- ITG Engineering Guidelines
- Introduction
- Network engineering guidelines overview
- ITG traffic engineering
- Configuration of Meridian 1 routes and network translation
- Assess WAN link resources
- QoS Evaluation Process Overview
- Set QoS
- Measure intranet QoS
- Implement QoS in IP networks
- ITG Trunk DSP profile settings
- Post-installation network measurements
- Estimate QoS level
- ITG MAT PC management configuration
- Install and configure ITG ISL Trunk node
- Before you begin
- Installation Procedure Summary
- Create the ITG Trunk Installation Summary Sheet
- Install and cable ITG trunk cards
- Install NTCW84JA Large System I/O Panel 50-Pin filter adapter
- Install NTMF94EA and NTCW84KA cables
- D-channel cabling for the NT0961AA 24-Port ITG Trunk card
- Set NT6D80 MSDL switches
- Install filter and NTND26 cable (for MSDL and DCHIP cards in same Large System equipment row)
- Install filter and NTND26 cable (for MSDL and DCHIP cards in different Large System equipment rows)
- Configure ITG Trunk data on the Meridian 1
- Configure dialing plans within the corporate network
- Configure ITG Trunk data on MAT
- Transmit ITG trunk card configuration data from MAT to the ITG trunk cards
- Set date and time for the ITG ISL Trunk node
- Change the default ITG shell password to maintain access security
- Change default ESN5 prefix for non-ESN5 IP telephony gateways
- Check card software
- Configure MAT Alarm Management to receive SNMP traps from ITG ISL Trunk cards
- Make test calls to the remote ITG nodes
- Upgrade an ITG Trunk 1.0 node to support ISDN signaling trunks
- Upgrade procedure summary
- Before you begin
- Install the DCHIP hardware upgrade kit
- Upgrade the 8-port ITG basic trunk software to ITG ISL trunk software
- Remove ITG 1.0 configuration data from Meridian 1
- Configure the Meridian 1 ITG ISL Trunk data: upgrade considerations
- Verify ROM-BIOS version
- Upgrade Troubleshooting
- OA&M using MAT applications
- OA&M using the ITG shell CLI and overlays
- Maintenance
- Appendix A: Calbe description and NT8D81BA cable replacement
- NTMF94EA E - LAN, T - LAN and Serial Port cable
- NTCW84KA E-LAN, T-LAN, DCH & Serial cable
- NTAG81CA Faceplate Maintenance cable
- NTAG81BA Maintenance Extender cable
- NTCW84EA DCH PC Card Pigtail cable
- NTMF04BA MSDL extension cable
- NTCW84LA and NTCW84MA upgrade cables
- Prevent ground loops on connection to external customer LAN equipment
- Replace cable NT8D81BA with NT8D81AA
- Tools list
- NT8D81BA cable removal procedures
- Appendix B: Environmental and electrical regulatory data
- Appendix C: Subnet mask conversion from CIDR to dotted decimal format
- Appendix D: Configure a Netgear RM356 modem router for remote access
- Index
- Back
Page 94 of
378
ITG Engineering Guidelines
553-3001-202 Standard 1.00 April 2000
Provisioning ITG ISL TIE trunks and routes
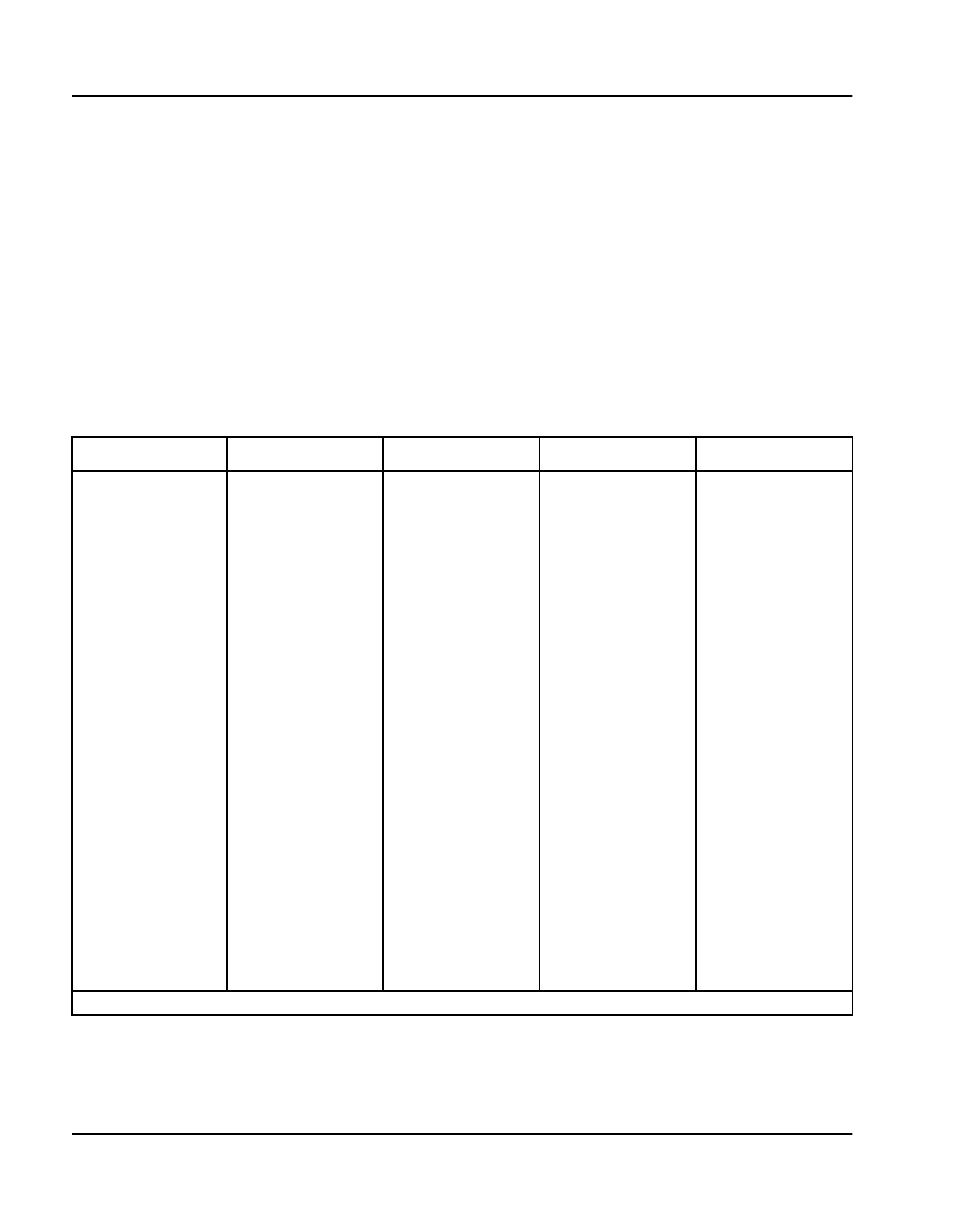
ITG ISL TIE trunks are provisioned based on average busy hour traffic tables,
using the calculated amount of traffic between ESN/ITG nodes. Table 12
shows the number of trunks required based on average busy hour CCS for a
1% blocking Grade of Service. Table 13 shows the number of trunks required
based on average busy hour CCS for a 10% blocking Grade of Service.
Note: A lower Grade of Service, such as P.10, may be preferred if
overflow routing is available through the PSTN, circuit-switched VPN,
or ITG ISL TIE trunks.
Table 12
Trunk traffic—Poisson 1 percent blocking Grade of Service (Part 1 of 2)
Trunks CCS Trunks CCS Trunks CCS Trunks CCS Trunks CCS
1 0.4 21 426 41 993 61 1595 81 2215
2 5.4 22 453 42 1023 62 1626 82 2247
3 15.7 23 480 43 1052 63 1657 83 2278
4 29.6 24 507 44 1082 64 1687 84 2310
5 46.1 25 535 45 1112 65 1718 85 2341
6 64 26 562 46 1142 66 1749 86 2373
7 84 27 590 47 1171 67 1780 87 2404
8 105 28 618 48 1201 68 1811 88 2436
9 126 29 647 49 1231 69 1842 89 2467
10 149 30 675 50 1261 70 1873 90 2499
11 172 31 703 51 1291 71 1904 91 2530
12 195 32 732 52 1322 72 1935 92 2563
13 220 33 760 53 1352 73 1966 93 2594
14 244 34 789 54 1382 74 1997 94 2625
15 269 35 818 55 1412 75 2028 95 2657
16 294 36 847 56 1443 76 2059 96 2689
17 320 37 876 57 1473 77 2091 97 2721
18 346 38 905 58 1504 78 2122 98 2752
19 373 39 935 59 1534 79 2153 99 2784
20 399 40 964 60 1565 80 2184 100 2816
Note:
For trunk traffic greater than 4427 CCS, allow 29.5 CCS per trunk.










