- LG Software Innovations Coffeemaker User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Revision history
- Contents
- About this guide
- Description
- System requirements
- List of ITG ISDN components
- Ordering rules and guidelines
- ITG ISL Trunk card description
- ITG ISL Trunk card physical description
- ISDN Signaling Link
- Dialing plans
- Quality of Service
- Fallback to alternate facilities
- Type of Service
- Fax support
- Remote Access
- Per-call statistics support using RADIUS Client
- SNMP MIB
- Codec profiles
- Security passwords
- ITG Engineering Guidelines
- Introduction
- Network engineering guidelines overview
- ITG traffic engineering
- Configuration of Meridian 1 routes and network translation
- Assess WAN link resources
- QoS Evaluation Process Overview
- Set QoS
- Measure intranet QoS
- Implement QoS in IP networks
- ITG Trunk DSP profile settings
- Post-installation network measurements
- Estimate QoS level
- ITG MAT PC management configuration
- Install and configure ITG ISL Trunk node
- Before you begin
- Installation Procedure Summary
- Create the ITG Trunk Installation Summary Sheet
- Install and cable ITG trunk cards
- Install NTCW84JA Large System I/O Panel 50-Pin filter adapter
- Install NTMF94EA and NTCW84KA cables
- D-channel cabling for the NT0961AA 24-Port ITG Trunk card
- Set NT6D80 MSDL switches
- Install filter and NTND26 cable (for MSDL and DCHIP cards in same Large System equipment row)
- Install filter and NTND26 cable (for MSDL and DCHIP cards in different Large System equipment rows)
- Configure ITG Trunk data on the Meridian 1
- Configure dialing plans within the corporate network
- Configure ITG Trunk data on MAT
- Transmit ITG trunk card configuration data from MAT to the ITG trunk cards
- Set date and time for the ITG ISL Trunk node
- Change the default ITG shell password to maintain access security
- Change default ESN5 prefix for non-ESN5 IP telephony gateways
- Check card software
- Configure MAT Alarm Management to receive SNMP traps from ITG ISL Trunk cards
- Make test calls to the remote ITG nodes
- Upgrade an ITG Trunk 1.0 node to support ISDN signaling trunks
- Upgrade procedure summary
- Before you begin
- Install the DCHIP hardware upgrade kit
- Upgrade the 8-port ITG basic trunk software to ITG ISL trunk software
- Remove ITG 1.0 configuration data from Meridian 1
- Configure the Meridian 1 ITG ISL Trunk data: upgrade considerations
- Verify ROM-BIOS version
- Upgrade Troubleshooting
- OA&M using MAT applications
- OA&M using the ITG shell CLI and overlays
- Maintenance
- Appendix A: Calbe description and NT8D81BA cable replacement
- NTMF94EA E - LAN, T - LAN and Serial Port cable
- NTCW84KA E-LAN, T-LAN, DCH & Serial cable
- NTAG81CA Faceplate Maintenance cable
- NTAG81BA Maintenance Extender cable
- NTCW84EA DCH PC Card Pigtail cable
- NTMF04BA MSDL extension cable
- NTCW84LA and NTCW84MA upgrade cables
- Prevent ground loops on connection to external customer LAN equipment
- Replace cable NT8D81BA with NT8D81AA
- Tools list
- NT8D81BA cable removal procedures
- Appendix B: Environmental and electrical regulatory data
- Appendix C: Subnet mask conversion from CIDR to dotted decimal format
- Appendix D: Configure a Netgear RM356 modem router for remote access
- Index
- Back
Page 100 of
378
ITG Engineering Guidelines
553-3001-202 Standard 1.00 April 2000
This assumes no correlation and no synchronization of voice bursts in
different simultaneous calls. This assumes some statistical model of
granularity and distribution of voice message bursts due to silence
suppression.
The following example illustrates the calculation procedure for Santa Clara
and Richardson. The total traffic on this route is 60 CCS. To use the preferred
codec of G.729 Annex AB with 30 ms payload, the bandwidth use on the
WAN is 11.2 kbit/s. WAN traffic is calculated using the following formula:
(60/36)*11.2 = 18.7 kbit/s. Augmenting this number by 30% would give us
the peak traffic rate of 24.3 kbit/s. This is the incremental bandwidth required
between Santa Clara and Richardson to carry the 60 CCS voice traffic during
the busy hour.
Assume that 20 CCS of the 60 CCS between Santa Clara and Richardson is
fax traffic. Of the 20 CCS, 14 CCS is from Santa Clara to Richardson, and 6
CCS is from Richardson to Santa Clara. What is the WAN data rate required
between those two locations?
Traffic between the two sites can be broken down to 54 CCS from Santa Clara
to Richardson, and 46 CCS from Richardson to Santa Clara, with the voice
traffic 40 CCS (=60-20) being the two-way traffic.
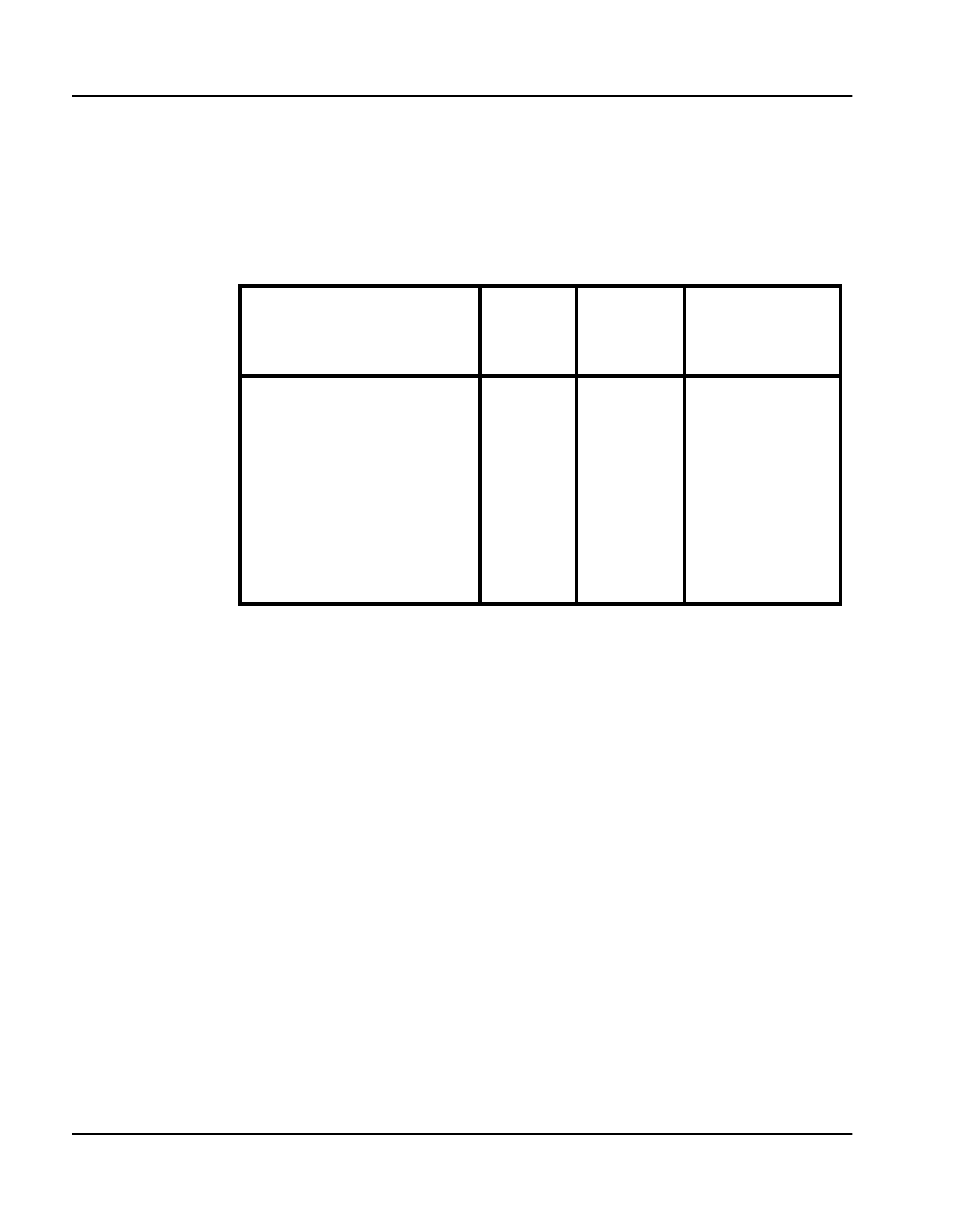
Table 16
Example: Incremental WAN bandwidth requirement
Destination Pair
CCS on
WAN
WAN
traffic in
kbit/s
Peaked WAN
traffic (x1.3) in
kbit/s
Santa Clara/Richardson 60 18.7 24.3
Santa Clara/Ottawa 45 14.0 18.2
Santa Clara/Tokyo 15 4.7 6.1
Richardson/Ottawa 35 10.9 14.2
Richardson/Tokyo 20 6.2 8.1
Ottawa/Tokyo 18 5.6 7.3










